Understanding Micro Partitioning and Clustering in Snowflake
Understanding Micro Partitioning and Clustering in Snowflake
Understanding Micro Partitioning and Clustering in Snowflake
Introduction to Partitioning in Databases
Partitioning in databases is a critical technique for managing large datasets. It divides large tables into smaller, more manageable pieces, called partitions, to improve performance, reduce query times, and increase scalability. Traditional database systems like Oracle, SQL Server, and MySQL support partitioning, but they come with their own limitations and complexities. Snowflake, a cloud-based data warehouse, uses a more advanced approach called micro partitioning, alongside clustering, to handle large amounts of data efficiently.
In this article, we will dive into the concepts of micro partitioning and clustering in Snowflake, explain how they work, and provide examples to illustrate their benefits.
What is Micro Partitioning in Snowflake?
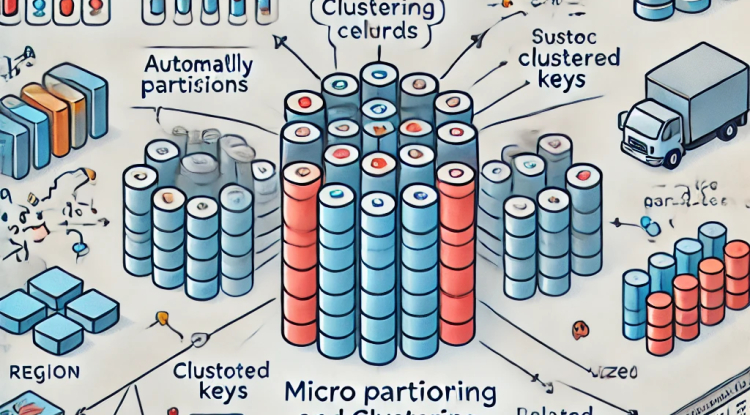
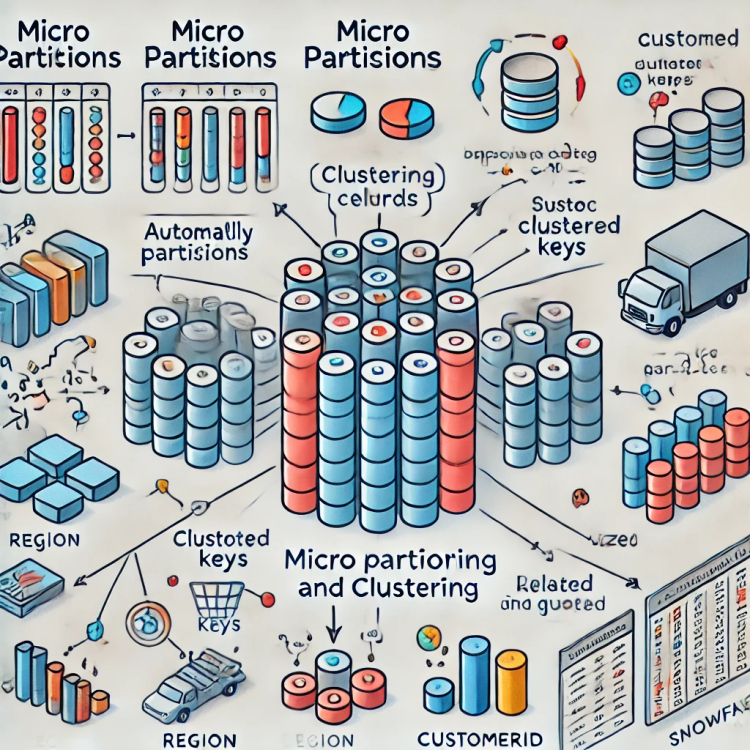
In Snowflake, micro partitioning is the process of dividing tables into small, immutable blocks of data that are stored on disk. These blocks are automatically created by Snowflake when data is loaded into a table. Unlike traditional partitioning, where the user explicitly defines partitioning criteria, micro partitioning happens automatically, based on the data being loaded. This automated approach eliminates the need for manual intervention and simplifies database management.
Key Characteristics of Micro Partitioning:
- Immutable: Once a micro partition is created, it cannot be changed. Any updates to the data result in the creation of a new micro partition.
- Size: Each micro partition typically holds between 50 MB and 500 MB of uncompressed data. Snowflake strives to keep each micro partition approximately 500 MB, though the actual size can vary depending on the data being loaded.
- Columnar Storage: Snowflake stores data in a columnar format. Each micro partition contains columnar data blocks, which allows for efficient query performance when only a few columns are accessed.
How Micro Partitioning Works
Let's consider an example: a Customer table containing information about customers and their purchases. This table may have columns like CustomerID, Name, Email, Address, and PurchaseAmount.
When data is loaded into Snowflake, it is stored in micro partitions. Each micro partition may contain a few thousand rows of data. Snowflake automatically manages the distribution of these rows across micro partitions, without any user intervention.
Suppose the Customer table contains 10 GB of data. As the data is loaded into Snowflake, it is divided into 20 micro partitions, each holding 500 MB of data. When you query this table, Snowflake scans only the relevant micro partitions, which significantly improves query performance.
Benefits of Micro Partitioning
-
Improved Query Performance: Since data is divided into small, manageable chunks, queries that only need to access certain parts of the data can skip irrelevant micro partitions. This is known as partition pruning or partition elimination. By accessing only the relevant partitions, Snowflake can process queries much faster.
-
Automatic Management: Micro partitioning happens automatically when data is loaded into Snowflake, removing the need for database administrators to manually define partitions. This reduces the administrative overhead and ensures that partitioning is always optimized.
-
Efficient Storage: Micro partitions help avoid data skewness, a common problem in traditional partitioning where some partitions grow disproportionately larger than others. Since Snowflake automatically manages partition size, it ensures that data is evenly distributed across micro partitions.
What is Clustering in Snowflake?
While micro partitioning deals with how data is physically stored, clustering is a technique that optimizes the way data is organized and retrieved. Clustering in Snowflake involves defining a clustering key, which is a set of columns that Snowflake uses to organize data within micro partitions.
Clustering helps improve query performance by making it easier for Snowflake to locate relevant data. It works by ensuring that similar values in the clustering key are stored together within a micro partition. For example, if you frequently query a Sales table by Region, you could define Region as a clustering key to improve query performance for region-based queries.
Key Characteristics of Clustering:
-
Clustering Key: The clustering key is a set of one or more columns that Snowflake uses to order data within each micro partition. Unlike traditional databases, Snowflake automatically manages clustering behind the scenes.
-
Automatic Clustering: Snowflake automatically maintains clustering for tables that have a clustering key. Users don’t need to manually reorganize data or rebuild indexes.
-
Improved Query Efficiency: Clustering helps improve query performance by ensuring that related data is stored together. For example, queries that filter by the clustering key will be faster because the relevant data is likely stored in contiguous blocks.
How Clustering Works
Consider a scenario where you have a Sales table with the following columns: TransactionID, Region, ProductID, and SaleAmount. If you frequently run queries to filter by Region, you can define Region as the clustering key. Snowflake will then try to store the data in such a way that records with the same Region value are stored together within a micro partition.
For example:
- Records with
Region = USwill be clustered together in one or more micro partitions. - Records with
Region = UKwill be stored in another micro partition.
When you run a query that filters by Region, Snowflake will be able to efficiently access only the relevant micro partitions that contain data for the requested region.
Benefits of Clustering
-
Faster Queries: When querying data based on the clustering key, Snowflake can quickly locate and scan only the relevant micro partitions. This reduces the amount of data that needs to be processed, resulting in faster queries.
-
Efficient Storage: Clustering helps Snowflake minimize the amount of storage used by ensuring that related data is grouped together in micro partitions. This reduces the need for unnecessary data duplication.
-
No Manual Maintenance: Snowflake automatically manages clustering, so you don’t need to manually create or rebuild indexes as you would in traditional databases. This simplifies database management.
Example: Combining Micro Partitioning and Clustering
Let's imagine you are working with a Customer table in Snowflake, which stores customer information and their orders. You frequently query this table by Region and CustomerID. To optimize these queries, you could define Region and CustomerID as clustering keys.
-
Micro Partitioning: Snowflake automatically divides the
Customertable into micro partitions. Each partition holds 50 MB to 500 MB of data, which can include customer details likeCustomerID,Name, andEmail. -
Clustering: By defining
RegionandCustomerIDas clustering keys, Snowflake ensures that customers from the same region and with similarCustomerIDvalues are stored together within micro partitions. This clustering optimizes queries that filter byRegionandCustomerID, as Snowflake can efficiently scan the relevant partitions.
Conclusion
Micro partitioning and clustering are powerful features in Snowflake that help optimize data storage and query performance. Micro partitioning automatically divides data into small, immutable blocks, while clustering ensures that related data is stored together within each micro partition. Together, these features improve query efficiency, reduce storage costs, and simplify database management. By leveraging micro partitioning and clustering, Snowflake provides an efficient and scalable solution for handling large datasets in a cloud-based environment.
In contrast to traditional partitioning methods, Snowflake’s automated approach to partitioning and clustering removes the complexity of manual configuration and ensures that data is always stored and queried in the most efficient way possible.
What's Your Reaction?